1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
|
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define SIZE(arr) (sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]))
#define N 1000
char stack[N];
int head = -1;
int isOperator(char op) {
switch (op) {
case '+':
case '-':
return 1;
case '*':
case '/':
return 2;
default:
return -1;
}
}
char *convertInfix2Postfix(char *infixExpression) {
char *postfixExpression = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * N);
char *pmove = postfixExpression;
int i = 0;
while (i < strlen(infixExpression)) {
if (isdigit(infixExpression[i])) {
while (isdigit(infixExpression[i])) {
*pmove++ = infixExpression[i++];
}
*pmove++ = ' ';
i++;
} else {
switch (infixExpression[i]) {
case '(':
stack[++head] = infixExpression[i];
break;
case ')':
while (stack[head] != '(') {
*pmove++ = stack[head--];
*pmove++ = ' ';
}
head--;
break;
default:
while (head != -1 && isOperator(stack[head]) >= isOperator(infixExpression[i])) {
*pmove++ = stack[head--];
*pmove++ = ' ';
}
stack[++head] = infixExpression[i];
}
i += 2;
}
}
while (head != -1) {
*pmove++ = stack[head--];
*pmove++ = ' ';
}
*pmove = '\0';
return postfixExpression;
}
void testConversion(char *infixExpression, char *expectedPostfix) {
char *postfixExpression = convertInfix2Postfix(infixExpression);
printf("中缀表达式: %s\n", infixExpression);
printf("转换后的后缀表达式: %s\n", postfixExpression);
printf("期望的后缀表达式: %s\n", expectedPostfix);
if (strcmp(postfixExpression, expectedPostfix) == 0) {
printf("测试通过 ✓\n\n");
} else {
printf("测试失败 ✗\n\n");
}
}
int main() {
testConversion("3 + 4", "3 4 + ");
testConversion("3 + 4 - 2", "3 4 + 2 - ");
testConversion("3 + 4 * 2", "3 4 2 * + ");
testConversion("( 3 + 4 ) * 2", "3 4 + 2 * ");
testConversion("( ( 3 + 4 ) * 2 )", "3 4 + 2 * ");
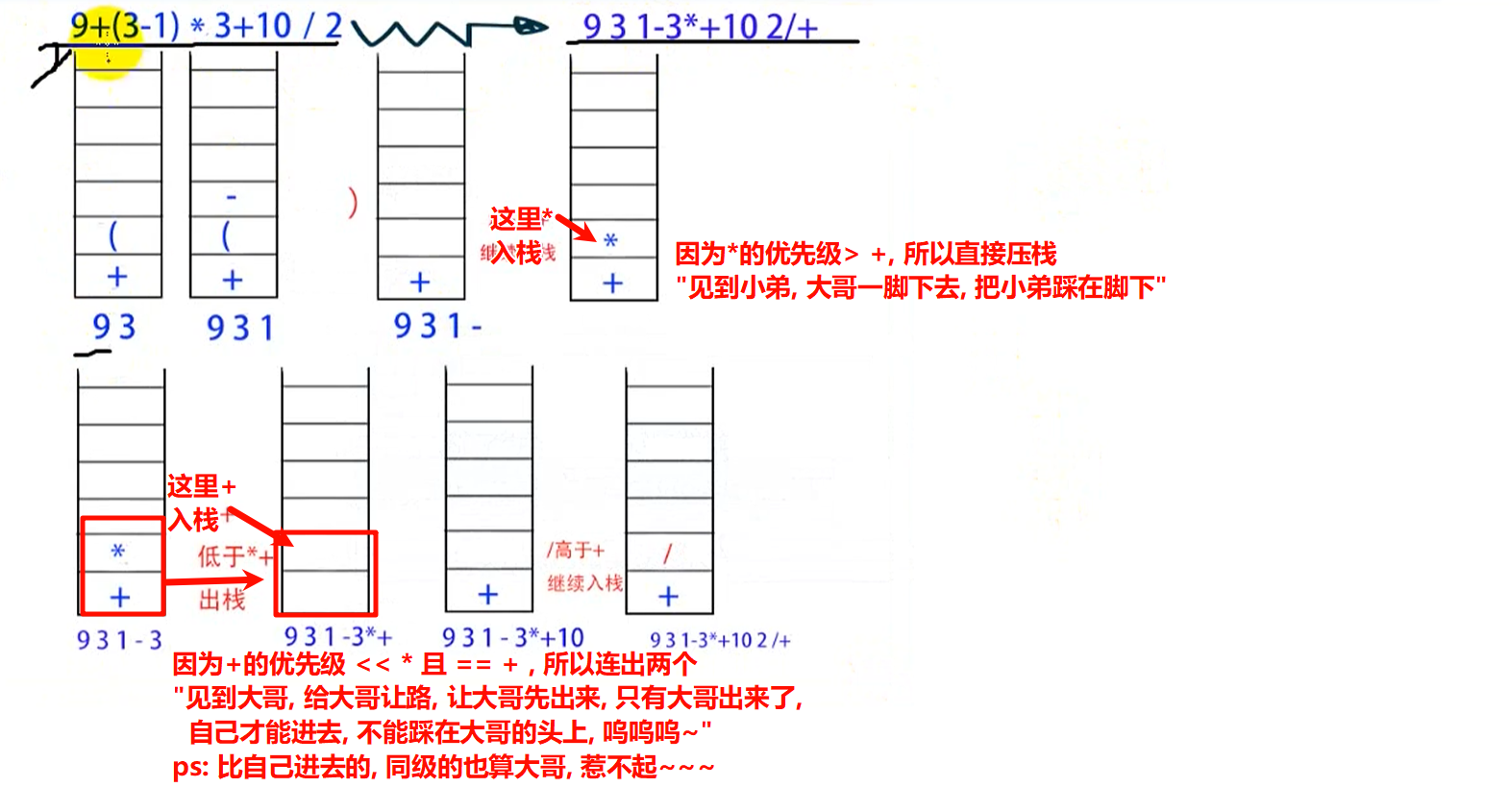
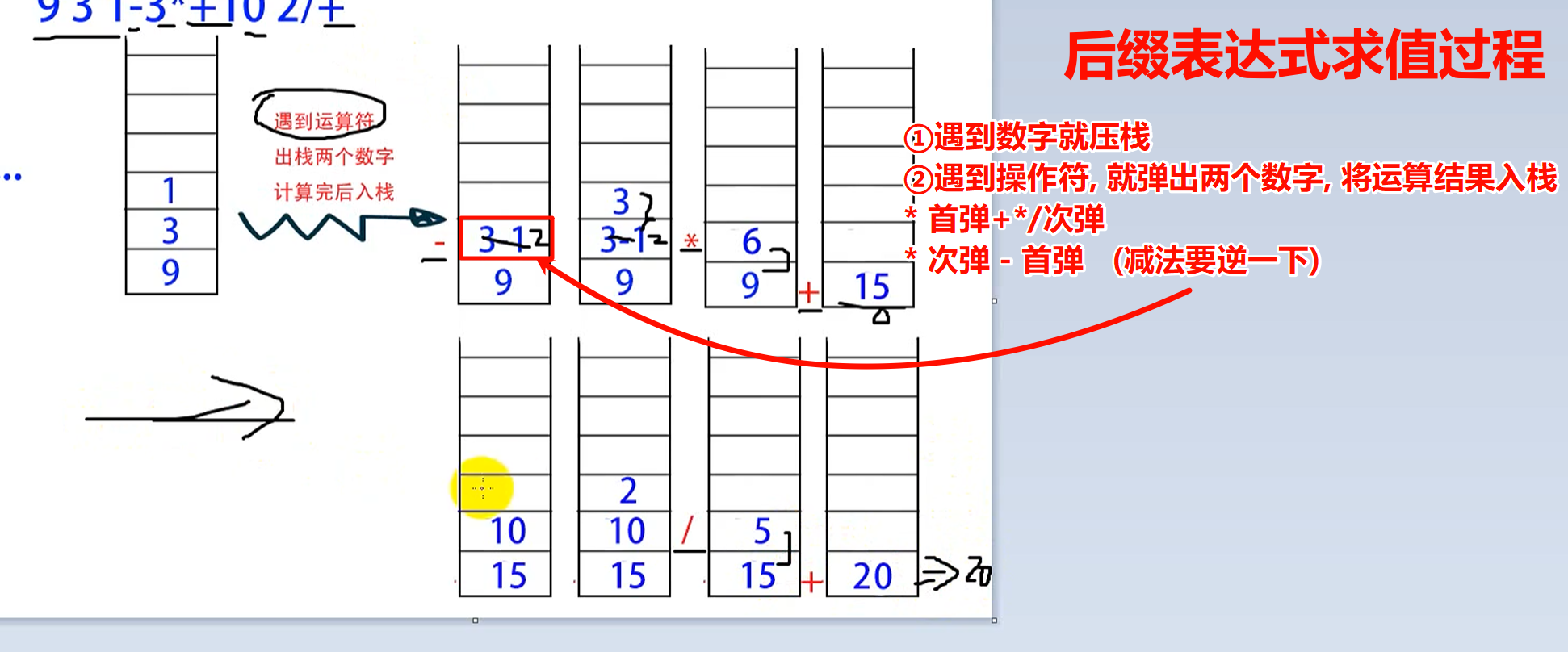
testConversion("9 + ( 3 - 1 ) * 3 + 10 / 2", "9 3 1 - 3 * + 10 2 / + ");
testConversion("5", "5 ");
testConversion("12 + 34", "12 34 + ");
testConversion("1 + 2 * 3 / 4 - 5", "1 2 3 * 4 / + 5 - ");
testConversion("1 - 2 - 3", "1 2 - 3 - ");
testConversion("", "");
return 0;
}
|