第一章 自测&关键词回顾
理论:①四个性质 ②如何变色 ③如何旋转 ④如何删除
实现:有头节点的三叉树 GCC红黑树实现
参考: 视频
- 大体思路:
- 头节点的parent域存储整棵树的根; data域表示为-1(或其他值/或你标识颜色也OK,更为保险); lrchild都不存东西;
- 这样维护, 在LRotation和RRotation时, 会方便维护parent节点; ==无需传递二级指针, 换根, 直接parent->l/rchild换即可==
第一节 红黑树的四个性质
- 四个性质:
- ① 是BST
- ②【根叶黑】根和叶子(NULL)必须是黑色
- ③【不红红】不存在连续的两个红色节点
- ④【黑路同】任意节点到叶子🍃所有路径,经过的黑色结点数量相同
- 两个结论:
- 从”整棵树”根到叶🍃的最长路径(尽可能多的红)<= 2* (“整棵树”根到叶🍃的最短路径(全黑)) 【因为“不红红”所以最长的路径上,红和黑节点个数相同】
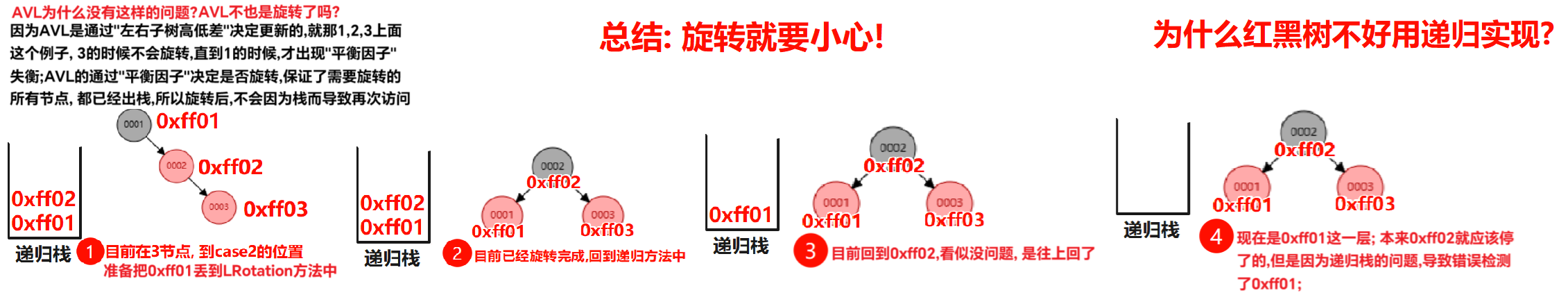
为什么维护这四个性质能使得”红黑树”在增删改的速度变快? 红黑树对比AVL的优势是什么? 视频
第二节 如何旋转
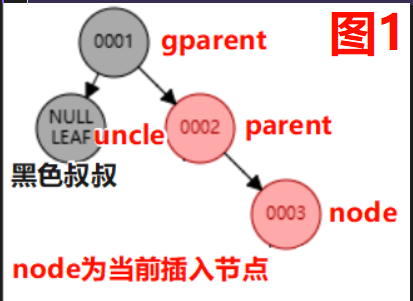
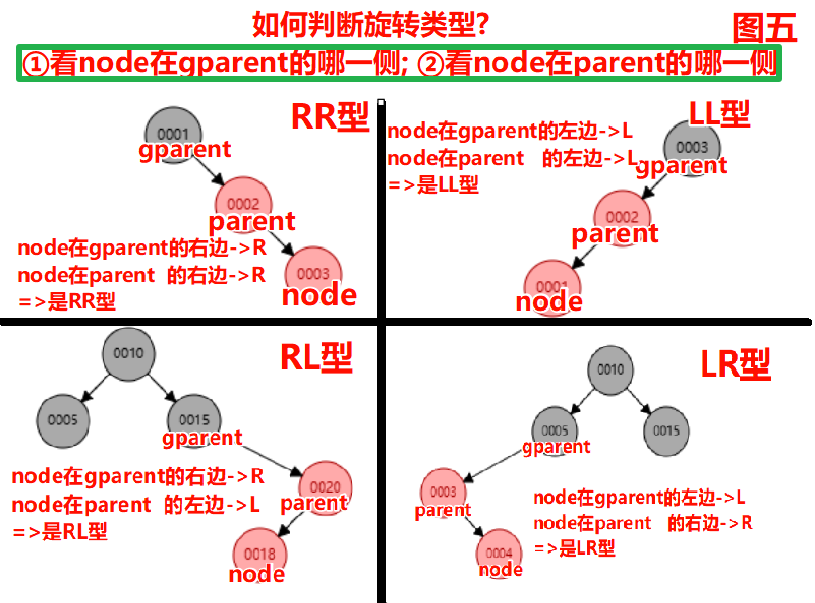
理论: 我们在插入的时候, 会有以下三种情况;其中只有case3与旋转有关; 节点说明如“图1”所示
实现: L/RRotation需要维护parent节点; 同时也需要维护parent到该节点(双向维护)

case1: 插入节点是根节点【违反 根叶黑】
调整方法: 根节点变黑
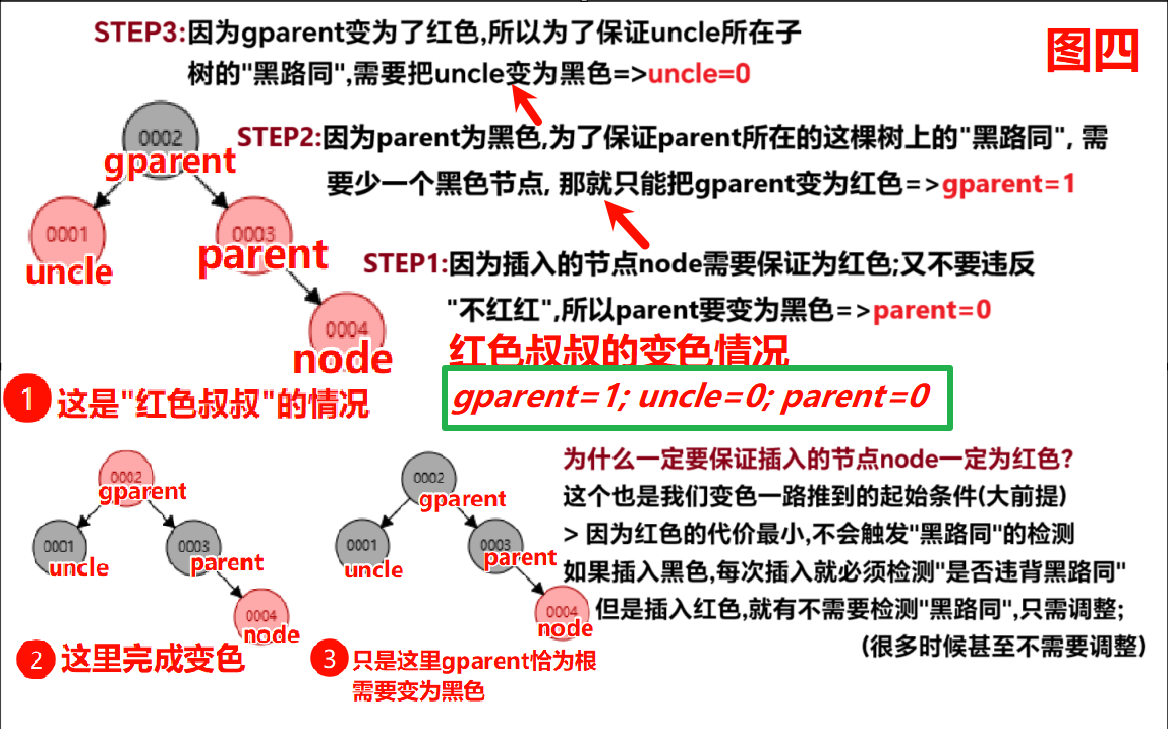
case2:插入节点的叔叔是红色【违反 不红红】
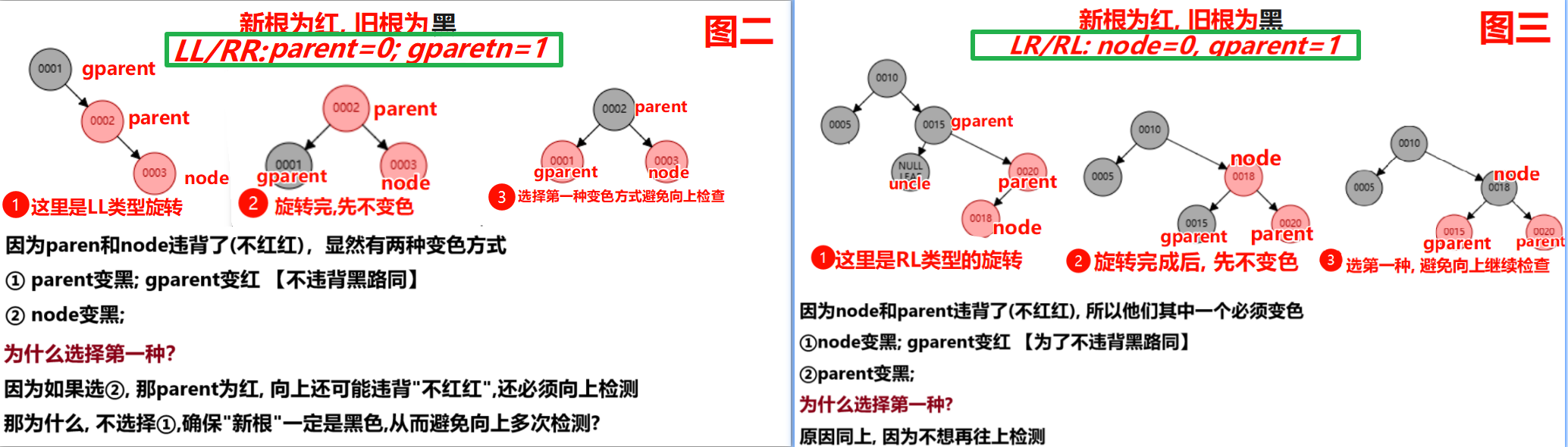
调整方法: ①gparent变为红色(1),parent和uncle变为黑色(0) ②让gparent节点变为插入的节点,继续向上检查
case3:插入节点的叔叔是黑色【违反 不红红】
调整方法: ①新根为黑色; 原根为红色 ②以node在gparetn和parent的位置;判断旋转类型
- 可见判断旋转类型, 无需通过平衡因子, 所以可以不维护
height属性

第三节 如何变色
我们在插入的时候, 会有以下三种情况;这里重点解释调整时的变色; 节点说明如“图1”所示
case1: 插入节点是根节点【违反 根叶黑】
调整方法: 根节点变黑
case2:插入节点的叔叔是红色【违反 不红红】
调整方法: ①gparent变为红色(1),parent和uncle变为黑色(0) ②让gparent节点变为插入的节点,继续向上检查

case3:插入节点的叔叔是黑色【违反 不红红】
调整方法: ①新根为黑色; 原根为红色 ②以node在gparetn和parent的位置;判断旋转类型
- 如何判断是否违背”黑路同”? 引入天外节点, 进行判断

第四节 如何实现”插入”方法
本质还是BST; 需要以下方法①BST插入(但要返回新增节点) ②fixRBTree(传入新节点):用于维护红黑树的性质 ③RRotation()和LRotation(): 用于旋转
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
TreeNode *init(int *input, int length) {
TreeNode *head = (TreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
head->parent = NULL;
head->data = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
TreeNode *newNod = insert(&(head->parent), *(input + i), head);
fixRBTree(head->parent, newNod);
}
return head;
}
|
1.4.1 BST插入(但要返回新增节点)
和BST一样: 只是需要返回新节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
TreeNode *insert(TreeNode **root, int x, TreeNode *parent) {
if (*root == NULL) {
TreeNode *newNode = (TreeNode *)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
newNode->data = x;
newNode->color = 1;
newNode->lchild = newNode->rchild = NULL;
newNode->parent = parent;
*root = newNode;
return newNode;
} else if (x < (*root)->data) {
return insert(&(*root)->lchild, x, *root);
} else {
return insert(&(*root)->rchild, x, *root);
}
}
|
1.4.2 fixRBTree(传入新节点)
关键方法: 用于维护红黑树的性质

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
void fixRBTree(TreeNode *root, TreeNode *node) {
TreeNode *newNode = root;
while (node->data != newNode->data) {
newNode = node->data < newNode->data ? newNode->lchild : newNode->rchild;
}
while (newNode->parent->data != -1 && newNode->parent->color == 1) {
TreeNode *parent = newNode->parent;
TreeNode *gparent = parent->parent;
TreeNode *uncle = gparent->lchild == parent ? gparent->rchild : gparent->lchild;
int uncleColor = uncle ? uncle->color : 0;
if (uncleColor == 1) {
parent->color = 0;
gparent->color = 1;
uncle->color = 0;
newNode = gparent;
continue;
}
else {
if (parent->data < gparent->data) {
if (newNode->data < parent->data) {
parent->color = 0;
gparent->color = 1;
RRotation(gparent);
} else {
newNode->color = 0;
gparent->color = 1;
LRotation(gparent->lchild);
RRotation(gparent);
}
} else {
if (newNode->data < parent->data) {
newNode->color = 0;
gparent->color = 1;
RRotation(gparent->rchild);
LRotation(gparent);
} else {
parent->color = 0;
gparent->color = 1;
LRotation(gparent);
}
}
break;
}
}
root->color = 0;
}
|
1.4.3 RRotation和LRotation(需要维护parent)
因为”红黑树”有parent,需要相较于AVL, 需要维护下parent即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
void LRotation(TreeNode *tree) {
TreeNode *root = tree;
TreeNode *rRChild = root->rchild;
TreeNode *orphan = rRChild->lchild;
TreeNode *outerNode = root->parent;
rRChild->lchild = root;
root->rchild = orphan;
if (orphan)
orphan->parent = root;
root->parent = rRChild;
rRChild->parent = outerNode;
if (outerNode->data == -1) {
outerNode->parent = rRChild;
} else {
if (outerNode->lchild == root) {
outerNode->lchild = rRChild;
} else {
outerNode->rchild = rRChild;
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
|
void RRotation(TreeNode *tree) {
TreeNode *root = tree;
TreeNode *rLChild = root->lchild;
TreeNode *orphan = rLChild->rchild;
TreeNode *outerNode = root->parent;
rLChild->rchild = root;
root->lchild = orphan;
if (orphan)
orphan->parent = root;
root->parent = rLChild;
rLChild->parent = outerNode;
if (outerNode->data == -1) {
outerNode->parent = rLChild;
} else {
if (outerNode->lchild == root) {
outerNode->lchild = rLChild;
} else {
outerNode->rchild = rLChild;
}
}
}
|
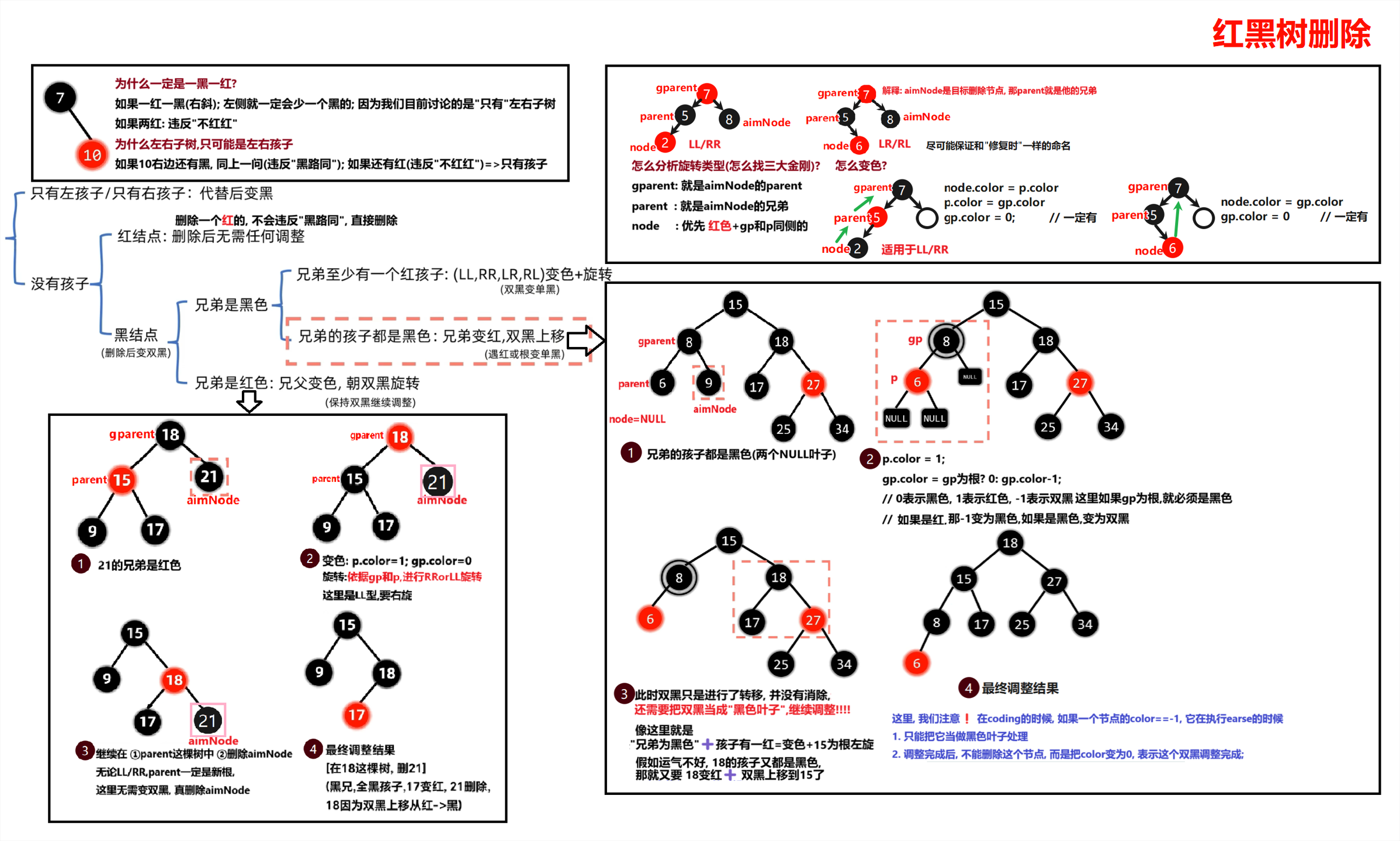
第五节 红黑树删除
这部分要推导比较困难(主播是笨蛋!),建议直接记住;

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
|
void earse(TreeNode *root, int x) {
TreeNode *aimNode = root;
while (x != aimNode->data) {
aimNode = x < aimNode->data ? aimNode->lchild : aimNode->rchild;
}
if ((aimNode->lchild == NULL && aimNode->rchild == NULL) || aimNode->color == -1) {
if (aimNode->parent->data == -1) {
aimNode->parent->parent = NULL;
return;
}
if (aimNode->color != 1) {
TreeNode *gparent = aimNode->parent;
TreeNode *parent = gparent->lchild == aimNode ? gparent->rchild : gparent->lchild;
TreeNode *node = NULL;
if (parent == gparent->lchild) {
if (parent->lchild && parent->lchild->color == 1)
node = parent->lchild;
else if (parent->rchild && parent->rchild->color == 1)
node = parent->rchild;
} else {
if (parent->rchild && parent->rchild->color == 1)
node = parent->rchild;
else if (parent->lchild && parent->lchild->color == 1)
node = parent->lchild;
}
if (parent->color == 1) {
parent->color = 0;
gparent->color = 1;
if (gparent->lchild == parent) {
RRotation(gparent);
} else {
LRotation(gparent);
}
earse(parent, x);
return;
}
else {
if (node != NULL) {
if (parent->data < gparent->data) {
if (node->data < parent->data) {
node->color = parent->color;
parent->color = gparent->color;
gparent->color = 0;
RRotation(gparent);
} else {
node->color = gparent->color;
gparent->color = 0;
LRotation(parent);
RRotation(gparent);
}
} else {
if (node->data < parent->data) {
node->color = gparent->color;
gparent->color = 0;
RRotation(parent);
LRotation(gparent);
} else {
node->color = parent->color;
parent->color = gparent->color;
gparent->color = 0;
LRotation(gparent);
}
}
}
else {
parent->color = 1;
gparent->color = gparent->parent->data == -1 ? 0 : gparent->color - 1;
if (gparent->color == -1)
earse(root, gparent->data);
}
}
}
if (aimNode->color != -1) {
if (aimNode->parent->lchild == aimNode)
aimNode->parent->lchild = NULL;
else
aimNode->parent->rchild = NULL;
} else {
aimNode->color = 0;
}
}
else if (aimNode->lchild != NULL && aimNode->rchild != NULL) {
TreeNode *successor = aimNode->rchild;
while (successor->lchild) {
successor = successor->lchild;
}
aimNode->data = aimNode->data ^ successor->data;
successor->data = aimNode->data ^ successor->data;
aimNode->data = aimNode->data ^ successor->data;
earse(aimNode->rchild, x);
}
else {
TreeNode *outerNode = aimNode->parent;
TreeNode *son = aimNode->lchild ? aimNode->lchild : aimNode->rchild;
son->color = 0;
if (outerNode->lchild == aimNode) {
outerNode->lchild = son;
} else {
outerNode->rchild = son;
}
son->parent = outerNode;
}
}
|
第二章 手撕
第三章 相关应用
第四章 上手真题
第五章 比赛怎么用