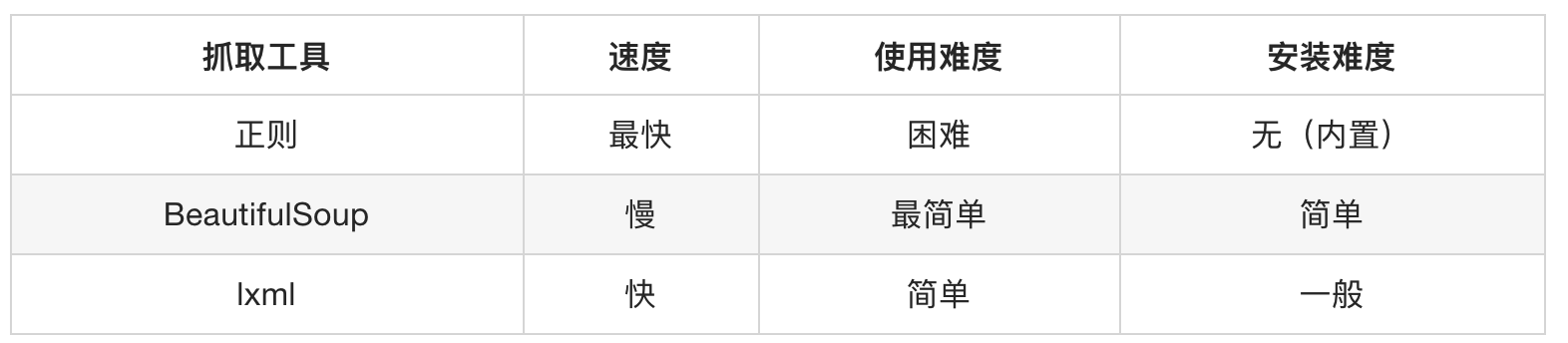
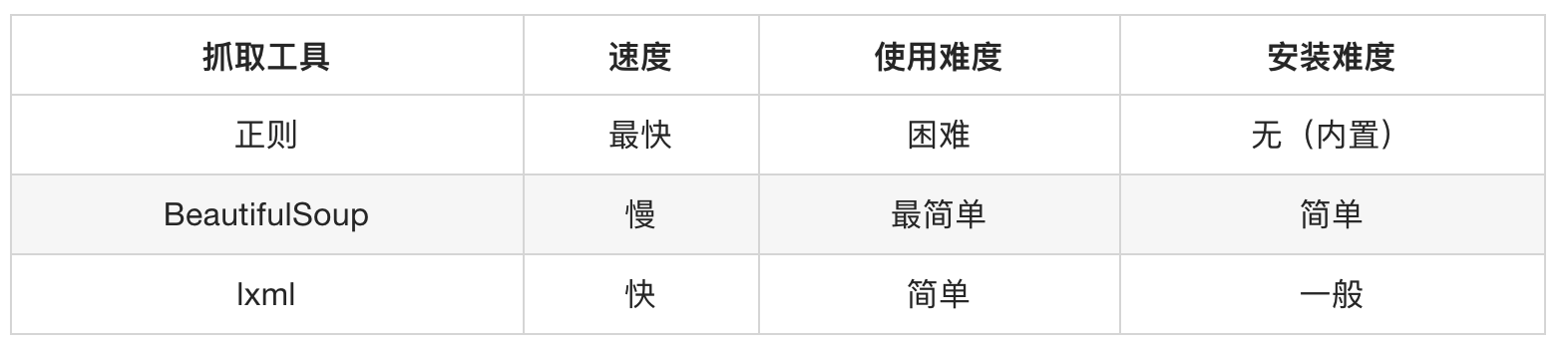
6.数据提取方式(xpaht,bs4)

第四章 Xpath lxml包
不是自带的, 需要下载
第一节 Xpath语法
4.1.1 语法规则
XPath使用路径表达式来选取文档中的节点或者节点集。这些路径表达式和我们在常规的电脑文件系统中看到的表达式非常相似。
| 表达式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
nodename |
选中该元素 |
/ |
从根节点选取、或者是元素和元素间的过渡 |
// |
从匹配选择的当前节点选择文档中的节点,而不考虑它们的位置 |
. |
选取当前节点 |
.. |
选取当前节点的父节点 |
@ |
选取属性 |
text() |
选取文本 |
路径表达式
| 路径表达式 | 结果 |
|---|---|
bookstore |
选择bookstore元素 |
/bookstore |
选取根元素 bookstore。注释:假如路径起始于正斜杠(/),则此路径始终代表到某元素的绝对路径! |
bookstore/book |
选取属于 bookstore 的子元素的所有 book 元素 |
//book |
选取所有 book 子元素,而不管它们在文档中的位置 |
bookstore//book |
选择属于 bookstore 元素的后代的所有 book 元素,而不管它们位于 bookstore 之下的什么位置 |
//book/title/@lang |
选择所有的book下面的title中的lang属性的值 |
//book/title/text() |
选择所有的book下面的title的文本 |
查询特定节点
| 路径表达式 | 结果 |
|---|---|
//title[@lang="eng"] |
选择lang属性值为eng的所有title元素 |
/bookstore/book[1] |
选取属于 bookstore 子元素的第1个 book 元素 |
/bookstore/book[last()] |
选取属于 bookstore 子元素的最后1个 book 元素 |
/bookstore/book[last()-1] |
选取属于 bookstore 子元素的==倒数第2个== book 元素 |
/bookstore/book[position()>1] |
选择bookstore下面的book元素,从第2个开始选择 |
/bookstore/book[position()>1 and position()<4] |
选择bookstore下面的book元素,从第2个开始取到第4个元素 |
//book/title[text()='Harry Potter'] |
选择所有book下的title元素,仅仅选择文本为Harry Potter的title元素 |
注意⚠️: 在
XPath中,第一个元素的位置是1,最后一个元素的位置是last(),倒数第二个是last()-1重点:
XPath的重点语法获取任意节点://XPath的重点语法根据属性获取节点:标签[@属性 = '值']XPath的获取节点属性值:@属性值XPath的获取节点文本值:text()
第二节 lxml包语法
使用
lxml包使用xpath语法做数据清洗的步骤
- STEP1: html语法的字符串=>
Element对象- STEP2: 调用
Element对象的.xpath("xpath语法")方法
4.2.1 html代码的字符串与Element对象的转化
语法:
需求 方法 返回值 字符串=> Elementelement对象 = etree.HTML("html代码的字符串")<class 'lxml.etree._Element'>Element=>字符串html代码的字符串=etree.tostring(html)<class 'bytes'>注意⚠️: 从element=>字符串的时候, 要是想转中文, 不能decode(), 没用, 得指定
etree.tostring()中encodeing属性值为unicode
from lxml import etree
html_string = ''' <div> <ul>
<li class="item-1">中文<a>first item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link2.html">second item</a></li>
<li class="item-inactive"><a href="link3.html">third item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link4.html">fourth item</a></li>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link5.html">fifth item</a>
</ul> </div> '''
# 一. string=>element
html = etree.HTML(html_string)
# 二. element=>string
string = etree.tostring(html) # 返回结果是<class 'bytes'>
string_unicode = etree.tostring(html, encoding="unicode") # 返回结果是<class 'str'>
4.2.2 Element对象使用xpath语法
- 语法:
Element.xpath("xpath语法) - 返回值:
<class 'list'>==列表==, 如果语法错误or没有内容🔙空列表
from lxml import etree
text = ''' <div> <ul>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link1.html">first item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link2.html">second item</a></li>
<li class="item-inactive"><a href="link3.html">third item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link4.html">fourth item</a></li>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link5.html">fifth item</a>
</ul> </div> '''
html = etree.HTML(text)
# 需求 提取`a标签`属性和文本
# 获取href的列表和title的列表
href_list = html.xpath("//li[@class='item-1']/a/@href")
title_list = html.xpath("//li[@class='item-1']/a/text()")
for title, href in zip(title_list, href_list): # zip()得保证一一对应, 否则乱
item = dict()
item["title"] = title
item["href"] = href
print(item)
4.2.3 XPath分次提取
前面我们取到属性,或者是文本的时候,返回字符串
但是如果我们取到的是一个节点,返回什么呢? 返回的是element对象,可以继续使用xpath方法
对此我们可以在后面的数据提取过程中:先根据某个xpath规则进行提取部分节点,然后再次使用xpath进行数据的提取
示例如下:
from lxml import etree
text = ''' <div> <ul>
<li class="item-1"><a>first item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link2.html">second item</a></li>
<li class="item-inactive"><a href="link3.html">third item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link4.html">fourth item</a></li>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link5.html">fifth item</a>
</ul> </div> '''
html = etree.HTML(text)
li_list = html.xpath("//li[@class='item-1']")
print(li_list)
# [<Element li at 0x2099d769908>, <Element li at 0x2099d769888>, <Element li at 0x2099d769988>]
可以发现结果是一个element对象(的列表),这个对象能够继续使用xpath方法
先根据li标签进行分组,之后再进行数据的提取
from lxml import etree
text = ''' <div> <ul>
<li class="item-1"><a>first item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link2.html">second item</a></li>
<li class="item-inactive"><a href="link3.html">third item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="link4.html">fourth item</a></li>
<li class="item-0"><a href="link5.html">fifth item</a>
</ul> </div> '''
html = etree.HTML(text)
li_list = html.xpath("//li[@class='item-1']")
print(li_list)
# 在每一组中继续进行数据的提取
for li in li_list:
item = dict()
item["href"] = li.xpath("./a/@href")[0] if len(li.xpath("./a/@href")) > 0 else None
item["title"] = li.xpath("./a/text()")[0] if len(li.xpath("./a/text()")) > 0 else None
print(item)
4.2.4 总结
lxml库的安装:pip install lxmllxml的导包:from lxml import etree;lxml转换解析类型的方法:etree.HTML(text)lxml解析数据的方法:data.xpath("//div/text()")- 需要注意
lxml提取完毕数据的数据类型都是列表类型 - 如果数据比较复杂:先提取大节点, 然后再进行小节点操作
第三节 作业
4.3.1 获取小说排行
需求: 获取小说网的
# =================================
# @Time : 2024年12月02日
# @Author : 明廷盛
# @File : 7.lxml(爬小说排行).py
# @Software: PyCharm
# @ProjectBackground: 需求爬取小说网[https://www.77xsw.com/top/all_0_1.html]的总榜(小说名称+小说链接)
# =================================
""" 分析
小说名称(xpath): //dd//h3//a/text()
小说链接(xpath): //dd//h3//a/@href 前缀: https://www.77xsw.com/
"""
from lxml import etree # xpath包
import requests
aim_url = "https://www.77xsw.com/top/all_0_1.html"
result = requests.get(aim_url).content.decode() # 网页的HTML代码
# 创建element对象, 该对象支持xpath语法
html = etree.HTML(result) # 为指定页面创建element对象 <class 'lxml.etree._Element'>
noval_name = html.xpath("//dd//h3//a/text()") # 获取"小说名称"
noval_link = html.xpath(" //dd//h3//a/@href") # 获取"小说链接"
noval_link = ["https://www.77xsw.com" + i for i in noval_link] # 拼接下链接的前缀
r1 = list(zip(noval_name, noval_link)) # zip()的返回值类型是 <class 'zip'>, 建议转为list用
# 打印结果
for i in r1:
print(i)
4.3.2 获取房源信息
需求: 用xpath做一个简单的爬虫,爬取链家网里的租房信息获取标题,位置,房屋的格局(三室一厅) ,关注人数,单价,总价
# =================================
# @Time : 2024年12月02日
# @Author : 明廷盛
# @File : 8.作业(爬取房源信息).py
# @Software: PyCharm
# @ProjectBackground:需求: 用xpath做一个简单的爬虫,爬取[链家网](https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/pudong/pg2/)
# 里的租房信息获取标题,位置,房屋的格局(三室一厅) ,关注人数,单价,总价
# =================================
import requests
from lxml import etree
""" xpath分析
答疑课提醒:
①一定要分组,xpath分组是什么意思? 前面想同( //div[@class='info clear'])一定都是单独的方框, 这尽管里面的数据有缺失, 也不会乱
②多个类,找xpath定位的优先级 id > 仅一个class > 多个class (因为页面渲染出来的html!=爬下来的源码html,类多个,可能不是源码的是渲染产生的)
③.//a 是从当前节点开始; //a是以html根节点开始(无论当前是否属于某个节点)
"""
aim_url = "https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/pudong/pg2/"
headers = {
"user-agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/131.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"cookie": "lianjia_uuid=3b7b0674-b1a6-447b-a435-09f10739b984; crosSdkDT2019DeviceId=-dse9ij-sbyxd0-lbsnz2mk5si5un3-dn1m2qusl; ftkrc_=eb2baf39-22f8-493c-b001-f1458f20af7e; lfrc_=bfc2c2a2-612a-4411-9ee5-892eb1dc9152; _ga=GA1.2.1794759318.1733126288; sensorsdata2015jssdkcross=%7B%22distinct_id%22%3A%221938660417f1d1c-03b2448eadc76-26011851-2359296-193866041801f5d%22%2C%22%24device_id%22%3A%221938660417f1d1c-03b2448eadc76-26011851-2359296-193866041801f5d%22%2C%22props%22%3A%7B%22%24latest_traffic_source_type%22%3A%22%E7%9B%B4%E6%8E%A5%E6%B5%81%E9%87%8F%22%2C%22%24latest_referrer%22%3A%22%22%2C%22%24latest_referrer_host%22%3A%22%22%2C%22%24latest_search_keyword%22%3A%22%E6%9C%AA%E5%8F%96%E5%88%B0%E5%80%BC_%E7%9B%B4%E6%8E%A5%E6%89%93%E5%BC%80%22%7D%7D; _ga_GVYN2J1PCG=GS1.2.1733126289.1.1.1733127368.0.0.0; _ga_LRLL77SF11=GS1.2.1733126289.1.1.1733127368.0.0.0; select_city=310000; lianjia_ssid=c0f3afe8-efb3-4bc0-98e3-d2ad09cc445a; Hm_lvt_46bf127ac9b856df503ec2dbf942b67e=1733126275,1733223449; HMACCOUNT=1B16DEE07AC062C0; login_ucid=2000000075296624; lianjia_token=2.0012c624dc6fd9a640036b0ded2a71dc29; lianjia_token_secure=2.0012c624dc6fd9a640036b0ded2a71dc29; security_ticket=Tt6J/9Y8dIAxqSlq9+5yvUNfTbTfoSKCbUp1ZSl4zHq6gzp+PvWu0I1U5Evm5azgqZRLyVhiwrGedwvvbpV6BTYUvgvSQfBFQZOnpAWFTZIiN8gf1ADeHxo0lAMkAeoHbgn2YTBHfENQjNKZ4YlqM9okf7h+exV0iRVFcWBFqEQ=; Hm_lpvt_46bf127ac9b856df503ec2dbf942b67e=1733223521"
}
html = requests.get(aim_url, headers=headers) # 获取页面
element = etree.HTML(html.content.decode()) # 获取element对象
# STEP1: 先分组
li_list = element.xpath('//ul[@class="sellListContent"]//li')
# STEP2: 遍历组中每条数据, 进行进一步数据清洗
house_list = []
for i in li_list:
one_house = {}
# 这里有两个需要注意的: ①.//是从当前节点下去找(这里必须用.)//是从html根节点去找 ②返回值是列表,要第一个值
one_house["title"] = i.xpath('.//div[@class="title"]/a/text()')[0]
one_house["positionInfo"] = '-'.join(i.xpath('.//div[@class="positionInfo"]/a/text()'))
one_house["houseInfo"] = i.xpath('.//div[@class="houseInfo"]/text()')[0]
one_house["followInfo"] = i.xpath('.//div[@class="followInfo"]/text()')[0]
one_house["unitPrice"] = i.xpath('.//div[@class="unitPrice"]//span/text()')[0]
one_house["totalPrice"] = i.xpath('.//div[@class="totalPrice totalPrice2"]//span/text()')[0]
house_list.append(one_house)
# STEP3: 输出数据
[print(i) for i in house_list]
第四节 使用xpath爬取的流程
4.4.1 STEP1: 先将目标爬取数据, 进行分组
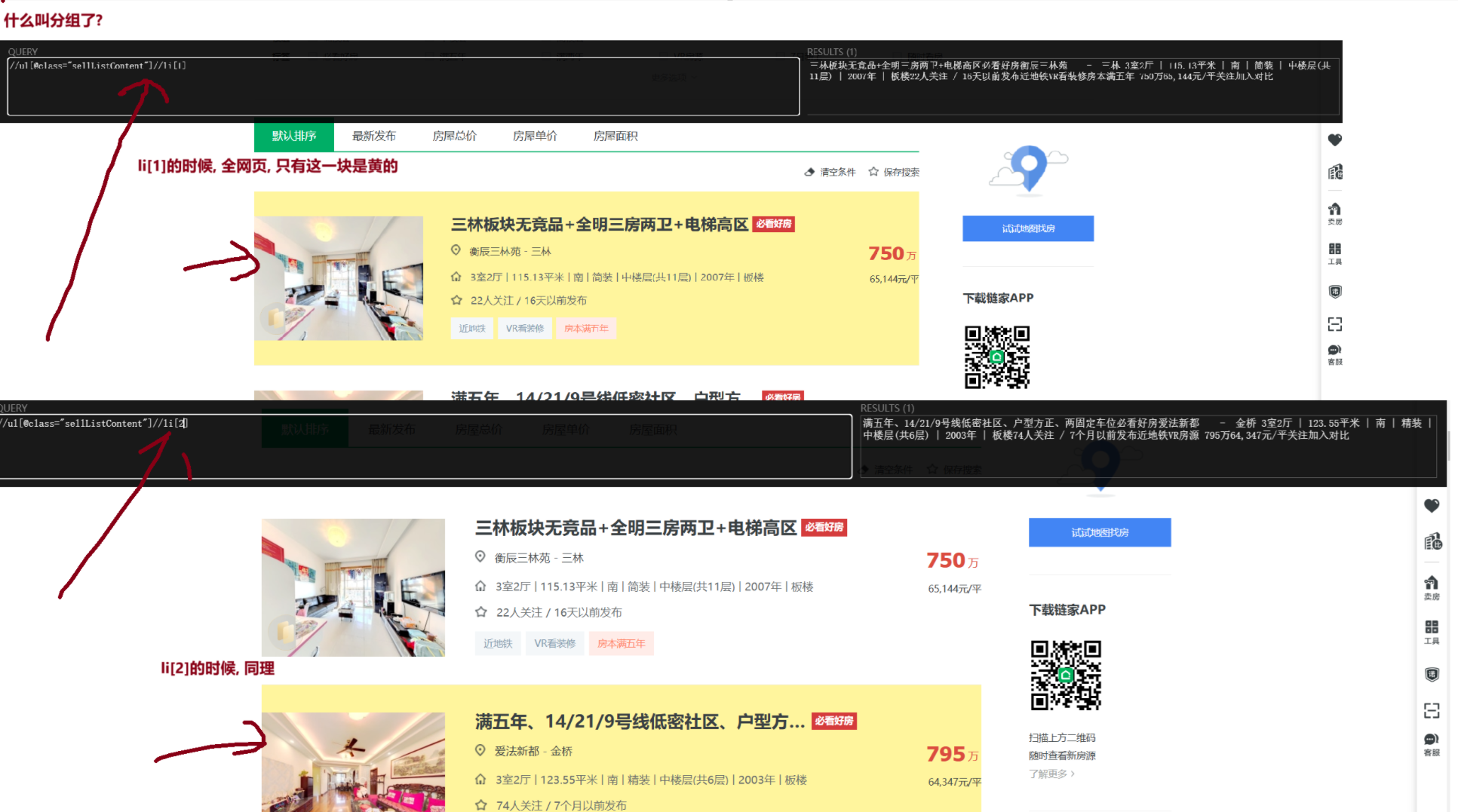
怎么检测是否分好组了? 这两个条件缺一不可
①页面上一个索引, 仅选中一块区域

②返回列表长度=需要爬取数据长度
li_list = element.xpath('//ul[@class="sellListContent"]//li')
print(len(li_list)) # 输出结果:30 页面正好有30个房源数据
4.4.2 STEP2 对组内每个元素操作.//
- 记住!! 一定是
.//这个才表示从当前节点开始模糊查询,//不管在哪, 是否有当前节点, 都是从html根开始模糊查询
第五章 易错点
- 定位数据的顺序: id > 仅一个class > 多个class (因为页面渲染出来的html!=爬下来的源码html,类多个,可能不是源码的是渲染产生的)
.//a是从**当前节点开始;//a是以html根节点开始**(无论当前是否属于某个节点)- ==返回的都是列表:== 无论是xpath语法中的
xpath()方法; 还是bs4语法中的find_all()/select();返回值都是列表!!!都是列表!!!都是列表!!!
第五章 BS4 bs4包
介绍
BeautifulSoup4简称BS4,和使用lxml模块 一样,Beautiful Soup 也是一个HTML/XML的解析器,主要的功能也是解析和提取HTML/XML数据。
Beautiful Soup是基于HTML DOM的,会载入整个文档,解析整个DOM树,因此时间和内存开销都会大很多,所以性能要低于lxml模块。
BeautifulSoup用来解析HTML比较简单,API非常人性化,支持CSS选择器、Python标准库中的HTML解析器,也支持 lxml模块的XML解析器
安装
pip install beautifulsoup4 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
官方文档:http://beautifulsoup.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/v4.4.0
第一节 创建BeautifulSoup对象
- 语法:
BeautifulSoup("html代码的字符串", "文档解析器")文档解析器可以是(“lxml”[推荐], “html.parser”, “html5lib”)
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
# 创建 Beautiful Soup 对象
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml")
print(type(soup)) # <class 'bs4.BeautifulSoup'>
print(soup.prettify()) # <class 'str'> 美化输出
第二节 获取HTML中的标签 find_all()
语法:
def find_all(self, name=None, attrs={}, recursive=True, string=None, limit=None, **kwargs)...
返回值:
<class 'bs4.element.ResultSet'>===列表==, 列表中每个元素的类型为<class 'bs4.element.Tag'>其他:
find()的用法与find_all一样,区别在于find返回第一个符合匹配结果,find_all则返回所有匹配结果的列表
5.2.1 按标签名称选择标签 name参数
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
# 需求一: 选取所有<a>标签
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml") # 创建 Beautiful Soup 对象
result = soup.find_all("a") # 选择所有的<a>标签
print(type(result)) # <class 'bs4.element.ResultSet'>是一个列表
for i in result:
print(i, type(i)) # <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>其中每个元素的类型
"""输出结果
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a> <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a> <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
"""
# 需求二: 获取含有 l的标签(html, li, ul) 支持正则
html2 = """
<html>
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup2 = bs4.BeautifulSoup(html2, "lxml")
result = soup2.find_all(re.compile(".*l.*")) # 支持正则表达式
print(result)
""" 输出结果:
[<html>
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>,
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
</ul>,
<li>1</li>,
<li>2</li>,
<li>3</li>]
"""
# 需求三: 只获取li和ul标签 [可传入列表]
result = soup2.find_all(['li', 'ul']) # 如果传递是一个列表,则`Beautiful Soup`会将与列表中任一元素匹配的内容返回。
print(result)
"""输出结果
[<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
</ul>,
<li>1</li>,
<li>2</li>,
<li>3</li>]
"""
5.2.2 按照属性选中标签 attrs参数
- 注意.⚠️: 简写的时候, 注意, 属性后又下划线
class_class
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml") # 创建 Beautiful Soup 对象
# 需求一. 获取class为sister的标签
ret_1 = soup.find_all(attrs={'class': 'sister'})
ret_2 = soup.find_all(class_='sister') # 简写,和上面等效
print(ret_1)
"""输出结果
[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
"""
# 需求二. 获取id属性为link2的标签
ret_3 = soup.find_all(id_='link2')
print(ret_3)
"""输出结果
[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>]
"""
# 需求三. 获取class为sister的<a>标签,可配合name使用
html2 = """
<p class='hhh'>ppp1</p>
<a class='hhh'>link1</a>
"""
soup2 = bs4.BeautifulSoup(html2, "lxml") # 可以配合name使用
ret_4 = soup2.find_all("a", attrs={"class": "hhh"})
print(ret_4) # 输出结果:[<a class="hhh">link1</a>]
5.2.3 配合文本内容选择标签 string参数
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml") # 创建 Beautiful Soup 对象
# 需求一: 选取,文本内容为"Elsie"的<a>标签 [配合name]
result = soup.find_all(name="a", string="Elsie")
print(result) # 输出结果:[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>]
# 需求二: 选取, 文本内容为"Tillie"且class属性为"sister"的标签 [配合attar]
result = soup.find_all(attrs={"class": "sister"}, string="Tillie")
print(result) # 输出结果: [<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
第三节 获取HTML中的标签select()
- 语法:
select("CSS选择器")接受一个字符串参数,该字符串是 CSS 选择器。 - 返回值:
<class 'list'>它返回一个==列表==,其中包含所有匹配的元素。如果没有找到匹配的元素,返回一个空列表。列表中每个元素的类型为<class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html = """
<html>
<head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story" style="color:red">...</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml") # 创建 Beautiful Soup 对象
# 需求一: [标签选择器] 选取所有的<a>标签
result = soup.select("a")
print(result)
"""输出结果
[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
"""
# 需求二: [类选择器] 选取所有class为story的标签
result = soup.select(".story")
print(result)
"""输出结果
[<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>,
<p class="story" style="color:red">...</p>]
"""
# 需求三: [id选择器] 选取所有id为link2的标签
result = soup.select("#link2")
print(result)
"""输出结果
[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>]
"""
# 需求四: [层级选择器] 选取class为story下的所有<a>标签
result = soup.select(".story a")
print(result)
"""输出结果
[<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>]
"""
# 需求五: [属性选择器] 选取具有class为stroy
result = soup.select("p[style=color:'red']")
print(result) # 输出结果:[<p class="story" style="color:red">...</p>]
第四节 获取属性/文本 <Tag>类
标签类:
<class 'bs4.element.Tag'>说明: 这个类是BeautifulSoup中的标签类, 是
find_all()和select()返回的列表中每个元素的属性常用方法:
作用 语法 获取文本 <Tag>.getText()获取指定元素的值 <Tag>.get("属性名称")html = """
<html>
<head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<h1 class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></h1>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "lxml") # 创建 Beautiful Soup 对象
result = soup.find_all('h1')
for i in result:
print(i, type(i)) # <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>其中每个元素的类型
tag_text = i.getText() # <class 'str'> 返回标签内的文本 # 输出结果:The Dormouse's story
tag_class = i.get("class") # <class 'list'> 返回指定属性的值 # 输出结果:['title']
print(tag_text, type(tag_text))
print(tag_class, type(tag_class))
第五节 bs4 分次提取
- 和xpath分次提取一样: 获取到某个节点元素后, 后续的select()的”CSS选择器语法”是相对于当前节点的;
不是相对根
# bs4①:分组
li_list = soup.select(".sellListContent li")
# bs4②:遍历组内每个元素(相对获取)
for i in li_list:
title = i.select(".title a")[0].getText()
print(title)
第六章 作业
5.5.1 获取”搜狗微信”文字标题
使用
BS4抓取搜狗微信下的所有文章标题
# =================================
# @Time : 2024年12月03日
# @Author : 明廷盛
# @File : 10.作业(抓搜索内容的标题).py
# @Software: PyCharm
# @ProjectBackground: 需求: 使用`BS4`抓取[搜狗微信](https://weixin.sogou.com/)下的所有文章标题
# =================================
import bs4
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
header = {
"user-agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/131.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
}
def search_title(key_word, page):
aim_url = f"https://weixin.sogou.com/weixin?query={key_word}&_sug_type_=1&type=2&page={page}&ie=utf8"
result = requests.get(aim_url, headers=header)
html = bs4.BeautifulSoup(result.content.decode(), "lxml") # 获取BeautifulSoup对象
text = html.select(".txt-box a")
for i in text:
print(i.getText())
if __name__ == '__main__':
search_title("java", 2) # 搜索内容为java,第二页的内容
5.5.2 获取”链家网”的房源信息
需求: 用bs4做一个简单的爬虫,爬取链家网里的租房信息获取标题,位置,房屋的格局(三室一厅) ,关注人数,单价,总价
# =================================
# @Time : 2024年12月04日
# @Author : 明廷盛
# @File : 12.作业bs4(爬取房源信息).py
# @Software: PyCharm
# @ProjectBackground:需求: 用bs4做一个简单的爬虫,爬取[链家网](https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/pudong/pg2/)
# 里的租房信息获取标题,位置,房屋的格局(三室一厅) ,关注人数,单价,总价
# =================================
import requests
import bs4
# 爬虫STEP1:确定目标网站
aim_url = "https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/pudong/pg2/"
headers = {
"user-agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/131.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"cookie": "lianjia_uuid=3b7b0674-b1a6-447b-a435-09f10739b984; crosSdkDT2019DeviceId=-dse9ij-sbyxd0-lbsnz2mk5si5un3-dn1m2qusl; ftkrc_=eb2baf39-22f8-493c-b001-f1458f20af7e; lfrc_=bfc2c2a2-612a-4411-9ee5-892eb1dc9152; _ga=GA1.2.1794759318.1733126288; sensorsdata2015jssdkcross=%7B%22distinct_id%22%3A%221938660417f1d1c-03b2448eadc76-26011851-2359296-193866041801f5d%22%2C%22%24device_id%22%3A%221938660417f1d1c-03b2448eadc76-26011851-2359296-193866041801f5d%22%2C%22props%22%3A%7B%22%24latest_traffic_source_type%22%3A%22%E7%9B%B4%E6%8E%A5%E6%B5%81%E9%87%8F%22%2C%22%24latest_referrer%22%3A%22%22%2C%22%24latest_referrer_host%22%3A%22%22%2C%22%24latest_search_keyword%22%3A%22%E6%9C%AA%E5%8F%96%E5%88%B0%E5%80%BC_%E7%9B%B4%E6%8E%A5%E6%89%93%E5%BC%80%22%7D%7D; _ga_GVYN2J1PCG=GS1.2.1733126289.1.1.1733127368.0.0.0; _ga_LRLL77SF11=GS1.2.1733126289.1.1.1733127368.0.0.0; select_city=310000; lianjia_ssid=c0f3afe8-efb3-4bc0-98e3-d2ad09cc445a; Hm_lvt_46bf127ac9b856df503ec2dbf942b67e=1733126275,1733223449; HMACCOUNT=1B16DEE07AC062C0; login_ucid=2000000075296624; lianjia_token=2.0012c624dc6fd9a640036b0ded2a71dc29; lianjia_token_secure=2.0012c624dc6fd9a640036b0ded2a71dc29; security_ticket=Tt6J/9Y8dIAxqSlq9+5yvUNfTbTfoSKCbUp1ZSl4zHq6gzp+PvWu0I1U5Evm5azgqZRLyVhiwrGedwvvbpV6BTYUvgvSQfBFQZOnpAWFTZIiN8gf1ADeHxo0lAMkAeoHbgn2YTBHfENQjNKZ4YlqM9okf7h+exV0iRVFcWBFqEQ=; Hm_lpvt_46bf127ac9b856df503ec2dbf942b67e=1733223521"
}
# 爬虫STEP2:模拟请求并获取数据
result = requests.get(aim_url, headers=headers)
soup = bs4.BeautifulSoup(result.content.decode(), "lxml")
# 爬虫STEP3:数据提取
# bs4①:分组
li_list = soup.select(".sellListContent li")
# bs4②:遍历组内每个元素(相对获取)
house_info_list = []
for i in li_list:
one_dict = {}
one_dict["title"] = i.select(".title a")[0].getText()
# positionInfo = i.select('.positionInfo a') 这样拿到的是两个数据, 分别是列表的第一个和第二个, 要手动拼接下
# [<a data-el="region" data-log_index="1" href="https://sh.lianjia.com/xiaoqu/5011000019532/" target="_blank">河滨小区 </a>,
# <a href="https://sh.lianjia.com/ershoufang/chuansha/" target="_blank">川沙</a>]
one_dict["positionInfo"] = i.select('.positionInfo a')[0].getText() + "-" + i.select('.positionInfo a')[1].getText()
one_dict["houseInfo"] = i.select('.houseInfo')[0].getText()
one_dict["followInfo"] = i.select('.followInfo')[0].getText()
one_dict["unitPrice"] = i.select('.unitPrice')[0].getText()
one_dict["totalPrice"] = i.select('.totalPrice span')[0].getText() + "万"
house_info_list.append(one_dict)
# 爬虫STEP4:数据存储(这里就打印示意下)
[print(i) for i in house_info_list]
- Title: 6.数据提取方式(xpaht,bs4)
- Author: 明廷盛
- Created at : 2026-02-12 01:17:04
- Updated at : 2025-02-09 21:22:00
- Link: https://blog.20040424.xyz/2026/02/12/🐍爬虫工程师/第一部分 爬虫基础/6.数据提取方式(xpaht,bs4)/
- License: All Rights Reserved © 明廷盛